Like eating the right foods and getting enough sleep at night, exercising regularly is important to live a healthy life.
However, moving your body isn’t easy if you’re in pain!
Millions of people in the world suffer from knee pain, which already makes everyday activities, like sitting or standing, a challenge – let alone exercising.
Fortunately, the research has been done, and we’ve discovered that there are healthy ways to move your body without increasing your knee pain.
Some exercises can even lead to relief from knee pain!
In this article, we’ll list which exercises you should avoid while living with knee pain. We’ll also share safer workout alternatives and introduce you to a minimally invasive solution for lasting pain relief.
Exercises to Avoid While Living With Knee Pain

Certain exercises can put excessive stress on your knee joint, worsening pain and potentially causing further damage.
To avoid or modify to prevent aggravating your condition, make sure you avoid the following types of exercises:
- High-impact activities, such as running, jumping, or aerobics that involve both feet leaving the ground simultaneously, should be avoided [1].
- Deep squats and lunges can also put excessive stress on your knee joint, leading to an increase in knee pain. This is especially true if you have weak quadriceps or poor form,[2].
- Knee-intensive sports, like basketball, soccer, or tennis, can also worsen knee pain[3].
While it is recommended to avoid these activities, this does not mean exercise is impossible! There are plenty of exercises you can do while living with knee pain.
Read on to learn more about these preferred activities for knee pain sufferers.
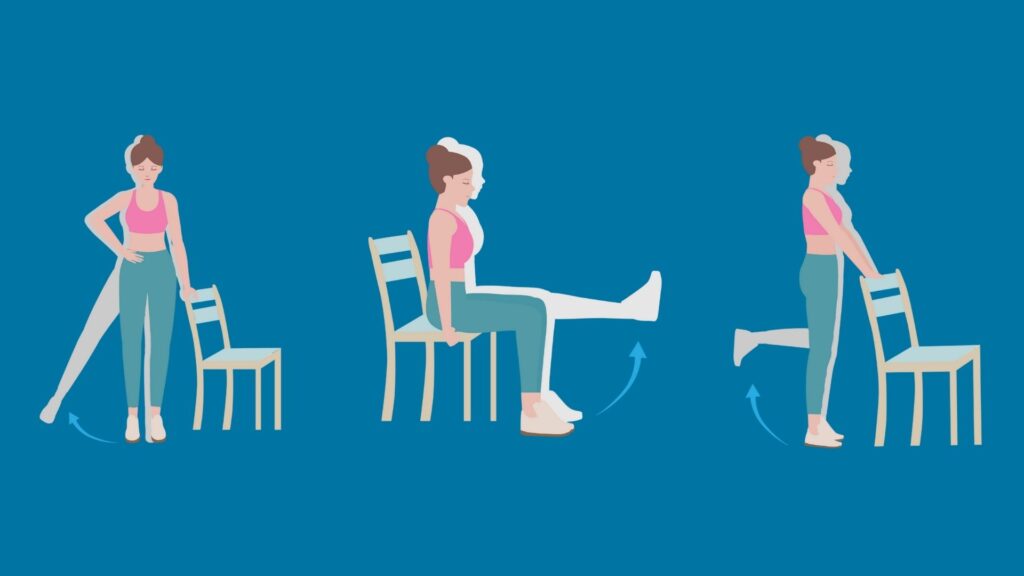

What Exercises Can I Do with Knee Pain?
Even while living with knee pain, exercise is still possible. Many safe and beneficial exercises can even help alleviate knee pain!
These are:
Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercises are fantastic low-impact options that can help improve cardiovascular fitness without putting extra stress on your knee joint[1]. Some examples of these activities include cycling, swimming, or using an elliptical trainer.
Strength Exercises
It’s important to build muscle! Strengthening exercises can help reduce pain and improve knee function[10].
Flexibility and Balance
Flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga or tai chi, can also help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness in your knee joint[4].
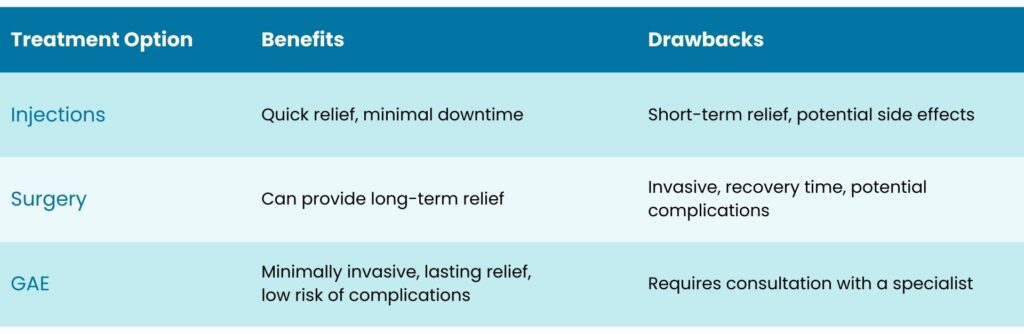
Knee Pain Relief Without Surgery
While exercise and physical therapy can provide relief, some people may require additional treatment options.
Traditional methods like injections can provide short-term relief, but they may have diminishing returns and are not a long-term solution.
Genicular artery embolization (GAE) is a minimally invasive procedure that can provide lasting relief from knee pain. GAE works by blocking blood flow to the affected area, reducing inflammation and pain[5].
How do these knee treatments compare? See below to compare the pros and cons of each:
Is GAE Right for You?
If you’re struggling with chronic knee pain and are interested in a long-term solution, consider meeting with one of the specialists at Centers for Knee Pain. Our team of experts can evaluate your current medical condition and help you determine if GAE is right for you.
You can also take our FREE online knee quiz to determine if you’re a potential candidate for GAE.
Conclusion
Knee pain can be debilitating, but it’s not a sign of weakness.
By avoiding exercises that exacerbate pain and incorporating safe alternatives, you can take the first step towards relief.
And when you’re ready to find a long-term solution to knee pain relief, Centers for Knee Pain is here to provide comprehensive and personalized care for you.
Remember, safe and effective pain relief options are available. You don’t have to live with knee pain!
Citations
- Gholami, Z., Faezi, S., Letafatkar, A., & Madreseh, E. (2023). Pain neuroscience education, blended exercises and booster sessions as an effective therapy for pain, functional and psychological factors in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a study protocol for a single-blind randomised controlled trial with 22 factorial design during 6-month follow-up. BMJ Open, 13. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-070336
- Thomas, K., Muir, K., Doherty, M., Jones, A., O’Reilly, S., & Bassey, E. (2002). Home based exercise programme for knee pain and knee osteoarthritis: randomised controlled trial. BMJ: British Medical Journal, 325(7367), 752. doi: 10.1136/bmj.325.7367.752
- Guo, X., Zhao, P., Zhou, X., Wang, J., & Wang, R. (2022). A recommended exercise program appropriate for patients with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Physiology, 13. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.934511
- Zhang, Y., Jordan, J. M., & Renner, J. B. (2010). The relationship between quadriceps strength and knee pain in people with knee osteoarthritis. Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy, 40(5), 257-265. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2010.3224
- Kim, H. J., Lee, S. C., & Kim, J. H. (2019). Genicular artery embolization for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 30(11), 1731-1741.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2019.06.015 …